|
News Camellian readings in St.Petersburg Photo Gallery |
Create iridariyaHomepage → Books on Iridarium (Iris Garden) → Look in the book → Create iridariya
Introduction
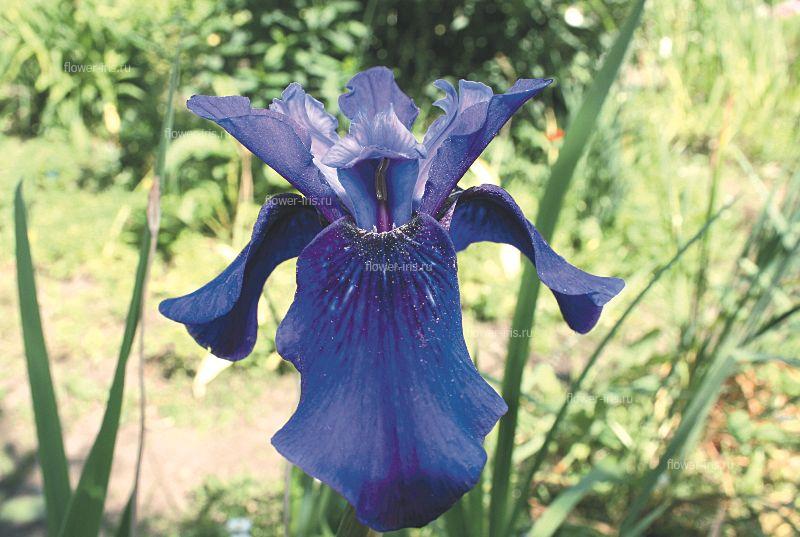
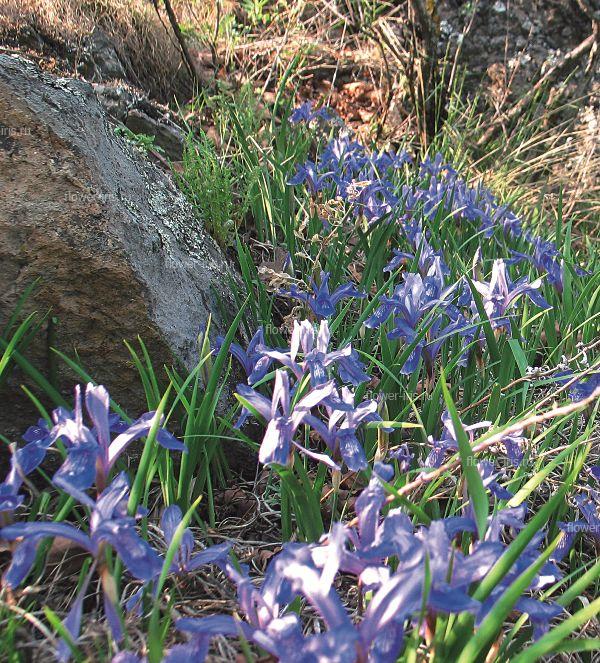
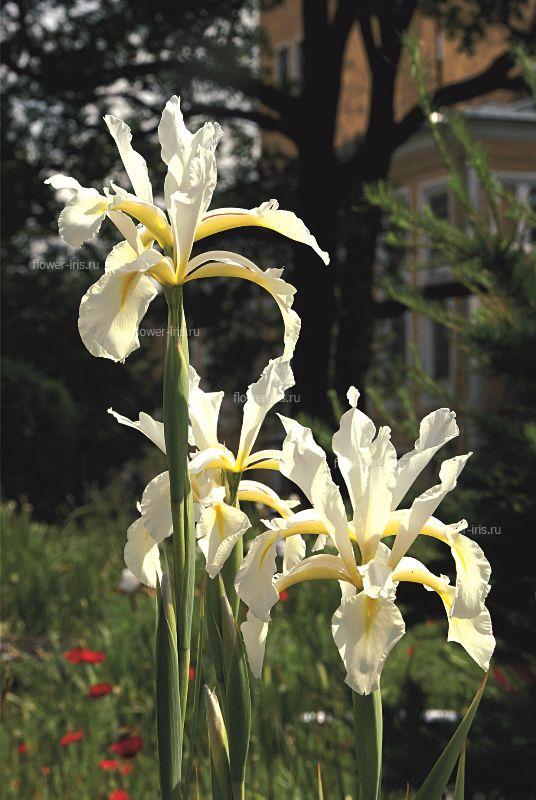
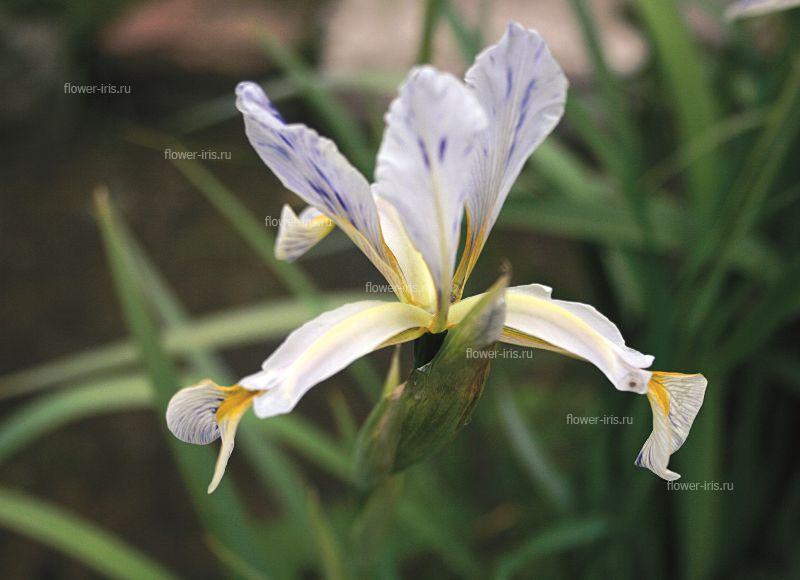
Create iridariya Family Iridaceae Bulbotubers Bulbous Rhizomatous Genus Iris Subgenus Iris Subgenus Limniris Subgenus Eremiris Subgenus Xyridion Subgenus Tenuifolia Genus Pardanthopsis The exhibition "Iris Russia" Exposure Iris garden Cultivate Insect Pests and diseases of Irises Literature The translation is done through the service translate.google.com. Before the war, irises were in the collection of perennials, which was in charge of OM Poletika. In the late 40's. Twentieth century GI Rodionenko as planned themes began collecting species and cultivars of the genus Iris (Iris). Over 15 years in the furrows of experimental site was a large garden unique collection not only iris (species, their geographical forms and varieties), but other members of the family Iridaceae. Addition of species and varietal composition occurs due to exchange with other botanical gardens, and in the course fees in nature. In total GI Rodionenko there were more than 15 expeditions. The most important of these was the expedition to the Primorsky Krai, as well as in remote mountain regions of the Caucasus and Central Asia. Exploring in detail the anatomical, morphological and biological characteristics of the iris, Rodionenko developing a new type, under which it is a native iris leaves only species with rhizomes and ensiform leaf blade. In 1961 appears the first domestic monograph "The Genus Iris - Iris L.» (Rodionenko, 1961a) and a popular edition of the irises in Russian (Rodionenko, 1961b). Active assistance in many experiments on the development of basic farming irises in the years exercised LP Lupanov gardener, she performed a large series of drawings for the monograph "Iris Rod." In the early 60's. the reconstruction of the Northern Court decided to set up collection sites exposition perennials. Exhibition Fund Iridariya consisted of the collection, grown on a large garden and planted in the north-western part of the Northern Court. Execution paths, decorative modules to include in the composition Iridariya various herbaceous perennials and with stones was suggested and done gardener RD Zubov care helped carry gardener LG Gromov. By this time, the collection consisted of 105 species and varieties of 23 genera and about 30 cultivars. Iridary reaches its peak in the 70's and 80's. The twentieth century. At that time, annual procurement varieties of iris from the leading foreign companies and breeding centers, to the Botanical Garden received gifts from local and foreign experts. As a result, variety collection has grown to 710 cultivars. In these years Iridarii tested over 2000 varieties of irises, received from England by Anne Blanco White (Anna Blanko White), from Vilnius to Eyher-Lorca, from Germany by Zeppelin (Zeppelin) and Thomas Tamberg (Tomas Tamberg), from Canada to Mack Murtha (McMurtrie), of the United States from Evan Mack (Mc Ewen) and family Schreiner (Schreiner's) - about 1,000 varieties of Japan from Mototeru Kamo (Mototeru Kamo) - 36 varieties I. ensata, as well as from the Main Botanical Garden of the USSR (Moscow) from N. Raikov and IV Aghajanian. Permanent expeditionary missions of the Botanical Garden Botanical them. Komarov Sciences in the Caucasus and Central Asia greatly enlarged exhibit new types and forms. By the late 80's. The twentieth century. collection already contains over 120 species and varieties of 37 genera. Excellent condition Iridariya in those years, of course, managed to maintain the dedicated more than 25 years of work by AN Zeksel. Smart combination of cultivation techniques to design art, she advocated Iridary all arranged in flower shows, winning prizes and receiving diplomas. One of the 20 registered varieties breeding GI Rodionenko Zeksel named Anna. First garden irises became the center of scientific research and a favorite destination of visitors Botanical Garden. During flowering irises is visited annually by 70 thousand people. From it was common in the botanical gardens, flower farms and hand fans of more than ten thousand specimens of variety iris rhizomes and different types of iris. Iridary irisovodstva becomes the center. Dvutomnik "Ornamental grasses" (1977) became a handbook for many gardeners, growers. It contains a detailed description of Iridaceae. Important role in promoting the culture of irises in Russia played the album "Iris" (Rodionenko, Dryagina et al, 1981). During perestroika begins the most difficult period for all of the collections of the Botanical Garden, including for Iridariya. In the late 80's - early 90's. reduced funding and, therefore, new acquisitions. For the same reason, stop and expeditionary travel. Collection funds are replenished mainly by seed exchange with other botanical gardens. Ability Iris quickly "run away" from the labels caused confusion in landing. However Iridary been saved. Plant care exercised ME Tikhonova, maintained at an appropriate level. Especially she was able to work with a group of Siberian irises. One of the books GI Rodionenko (co-authored with M. E. Tikhonova) was devoted mainly to this group (Rodionenko, Tikhonov, 1995). By the end of the 90s. on Iridarii left about 80 species and varieties of 20 genera and 400 cultivars of the genus Iris, many of which need to be checked and the variety of species belonging. In the late 90's. The twentieth century. the author of this book begins renovation work Iridariya. As planned topics for the introduction and protection of species of Iris (Iris) in Russia were gathering new material. An opportunity to field research: field observations were conducted in the North-West of Russia, in the Volga region, Northern Caucasus, Altai, Baikal, in the Far East (Alexeeva, 2004, 2006, 2007). Advice and assistance in the field work, kindly provided by the curators of botanical gardens in Barnaul, Vladivostok, Novosibirsk, Pyatigorsk, Stavropol, Chita, greatly facilitated the possibility of its collection Iridariya rare and poorly known flora of Russia. At the beginning of the twenty-first century. created geographic exposure irises collected in the European part of Russia and the North Caucasus, Siberia and Primorye to include some related plants natural flora. In addition, a complement to the collection varietal material. The first involved the initial variety of historical significance. At this time, one to identify varieties, 'escape' from the labels in the years of perestroika. Set up an exhibition area with grades GI Rodionenko and other domestic breeders. Restored collection of bulbous and klubnelukovichnyh species and varieties. Iridary is a rich base for scientific research. Of particular value is the collection of natural flora. From different, often difficult, parts of Russia were brought live plants and seeds. With Iridariya tested more than 120 species of 37 genera in the family Iridaceae (Alexeeva, 2001; Rodionenko, Alekseeva, 2002). At present, the collection includes more than 80 species and infraspecific taxa of the genus Iris natural flora and more than 450 cultivars, and about 30 species of other genera of this family. |


 Eng
Eng